 |
fpmas 1.6
|
 |
fpmas 1.6
|
#include <mutex.h>
Public Member Functions | |
| virtual T & | data ()=0 |
| virtual const T & | data () const =0 |
| virtual const T & | read ()=0 |
| virtual void | releaseRead ()=0 |
| virtual T & | acquire ()=0 |
| virtual void | releaseAcquire ()=0 |
| virtual void | lock ()=0 |
| virtual void | unlock ()=0 |
| virtual bool | locked () const =0 |
| virtual void | lockShared ()=0 |
| virtual void | unlockShared ()=0 |
| virtual int | sharedLockCount () const =0 |
| virtual void | synchronize ()=0 |
Protected Member Functions | |
| virtual void | _lock ()=0 |
| virtual void | _lockShared ()=0 |
| virtual void | _unlock ()=0 |
| virtual void | _unlockShared ()=0 |
Mutex API.
A Mutex protects (and allows) access to data instance of type T, using four semantic access rules :
In any case, concurrent access and data update management (potentially involving communications with other processes) are implementation defined, to allow the definition of several synchronization modes.
|
protectedpure virtual |
Internal lock function.
|
protectedpure virtual |
Internal lock shared function.
|
protectedpure virtual |
Internal unlock function.
|
protectedpure virtual |
Internal unlock shared function.
|
pure virtual |
Direct access to internal data representation.
Does not guarantee any concurrent access or data update management.
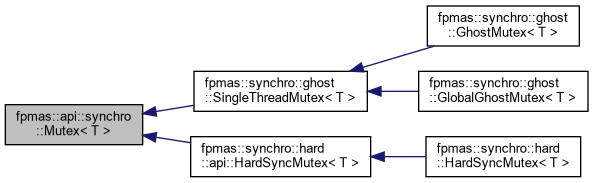
Implemented in fpmas::synchro::ghost::SingleThreadMutex< T >, and fpmas::synchro::hard::HardSyncMutex< T >.
|
pure virtual |
Direct access to internal data representation.
Does not guarantee any concurrent access or data update management.
Implemented in fpmas::synchro::ghost::SingleThreadMutex< T >, and fpmas::synchro::hard::HardSyncMutex< T >.
|
pure virtual |
Provides a read access to the internal data.
The functions blocks until data is effectively read.
Read data must be released using releaseRead().
Implemented in fpmas::synchro::ghost::GhostMutex< T >, fpmas::synchro::ghost::GlobalGhostMutex< T >, and fpmas::synchro::hard::HardSyncMutex< T >.
|
pure virtual |
Releases a mutex previously accessed with read().
Implemented in fpmas::synchro::ghost::GhostMutex< T >, fpmas::synchro::ghost::GlobalGhostMutex< T >, and fpmas::synchro::hard::HardSyncMutex< T >.
|
pure virtual |
Acquires an exclusive access to the internal data.
The function blocks until data is effectively acquired.
Write operations are semantically allowed on acquired data. However, how write operations are handled is implementation defined.
Acquired data must be released using releaseAcquire().
Implemented in fpmas::synchro::ghost::GhostMutex< T >, fpmas::synchro::ghost::GlobalGhostMutex< T >, and fpmas::synchro::hard::HardSyncMutex< T >.
|
pure virtual |
Releases a mutex previously accessed with acquire().
Semantically, this operation also "commits" eventual write operations that were performed on the acquired data. However, the actual behavior is implementation defined.
Implemented in fpmas::synchro::ghost::GhostMutex< T >, fpmas::synchro::ghost::GlobalGhostMutex< T >, and fpmas::synchro::hard::HardSyncMutex< T >.
|
pure virtual |
Locks the mutex.
This function blocks until internal data is effectively locked. Upon return, an exclusive access to the internal data is guaranteed. However, contrary to the acquire() function, this operation does not involve any data update or write operation handling.
A locked mutex must be unlocked using unlock().
Implemented in fpmas::synchro::ghost::SingleThreadMutex< T >, and fpmas::synchro::hard::HardSyncMutex< T >.
|
pure virtual |
Unlocks a mutex previously locked with lock().
Implemented in fpmas::synchro::ghost::SingleThreadMutex< T >, and fpmas::synchro::hard::HardSyncMutex< T >.
|
pure virtual |
Returns true if and only if the mutex has been locked and not yet unlocked.
Implemented in fpmas::synchro::ghost::SingleThreadMutex< T >, and fpmas::synchro::hard::HardSyncMutex< T >.
|
pure virtual |
Obtains a shared lock access to the mutex.
This function blocks until a shared lock access to mutex is effectively obtained. Contrary to lock(), multiple threads are allowed to simultaneously obtain a shared lock to the mutex.
The mutex must then be unlocked using unlockShared().
Implemented in fpmas::synchro::ghost::SingleThreadMutex< T >, and fpmas::synchro::hard::HardSyncMutex< T >.
|
pure virtual |
Unlocks a mutex previously locked with lockShared().
Semantically, all threads that called lockShared() must call unlockShared() to finally unlock the mutex.
Implemented in fpmas::synchro::ghost::SingleThreadMutex< T >, and fpmas::synchro::hard::HardSyncMutex< T >.
|
pure virtual |
Returns the count of threads that currently own a shared lock access to the mutex.
Implemented in fpmas::synchro::ghost::SingleThreadMutex< T >, and fpmas::synchro::hard::HardSyncMutex< T >.
|
pure virtual |
Method eventually called when data synchronization is performed on this Mutex.
The behavior of this method depends on the currently implemented SynchronizationMode.
Implemented in fpmas::synchro::ghost::GhostMutex< T >, fpmas::synchro::ghost::GlobalGhostMutex< T >, and fpmas::synchro::hard::HardSyncMutex< T >.